

In Anesthesia, Miller RD (ed), Philadelphia, Churchill-Livingstone, 2000. Anaesthesia 1974 29:494–495.Ĭote CJ: Pediatric anesthesia. Penlington GN: Endotracheal tube sizes for children. Thompson J, Craig N: Monitoring during mechanical ventilation In Capnography Clinical Aspects, Gravenstein JS, Jaffe MB, Paulus DA (Ed), Cambridge University Press, United Kingdom, 2004 pp59–64. We describe mainstream time-capnograph as an aid to recognize leak around the endotracheal tube and its utility to determine appropriate endotracheal tube size in small children.

Air-leak following tracheal intubation can be recognized by the presence of audible leak, by auscultation over the trachea, by palpation over the trachea and by observing effects of positive end-expiratory pressure on inspiratory expiratory tidal volume difference during mechanical ventilation.
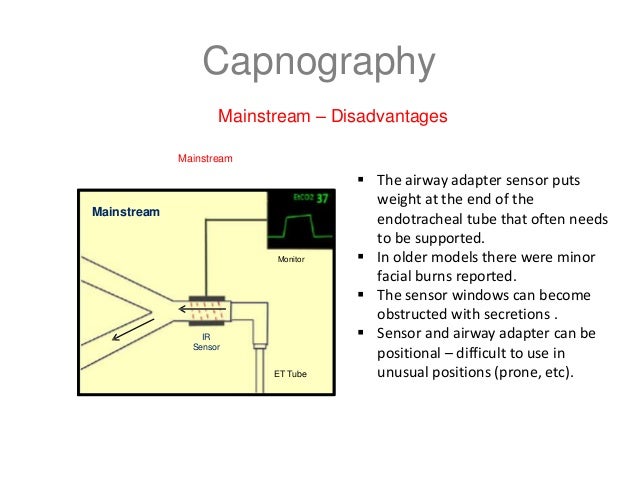
In children, for selecting an endotracheal tube, a variety of formulas and techniques are used to find the endotracheal tube size that minimizes both pressure induced tracheal injury and aspiration potential or variable ventilation. Therefore, it is desirable to intubate trachea with an appropriate but not an oversized endotracheal tube. However, uncuffed endotracheal tube may increase the risk of aspiration and lead to erratic delivery of preset tidal volume during mechanical ventilation. Indirectly, it reflects the production of CO2 by tissues and the circulatory transport of CO2 to the lungs.Uncuffed endotracheal tubes are commonly used in children in an attempt to decrease the potential for pressure induced tracheal injury. Capnography directly reflects the elimination of CO2 by the lungs to the anaesthesia device. The critical connection between the two components is either an endotracheal tube or a mask, and CO2 is typically monitored at this junction. In the presence of most forms of lung disease, and some forms of congenital heart disease the difference between arterial blood and expired gas increases and can exceed 1 kPa.ĭuring anaesthesia, there is interplay between two components: the patient and the anaesthesia administration device. In healthy individuals, the difference between arterial blood and expired gas CO2 partial pressures is very small. The capnogram is a direct monitor of the inhaled and exhaled concentration or partial pressure of CO2, and an indirect monitor of the CO2 partial pressure in the arterial blood. The plot may also show the inspired CO2, which is of interest when rebreathing systems are being used. It is usually presented as a graph of expiratory CO2 plotted against time, or, less commonly, but more usefully, expired volume. Its main development has been as a monitoring tool for use during anaesthesia and intensive care. In the presence of most forms of lung disease, and some forms of congenital heart disease (the cyanotic lesions) the difference between arterial blood and expired gas increases which can be an indication of new pathology or change in the cardiovascular-ventilation system.įreebase Rate this definition: 0.0 / 0 votesĬapnography is the monitoring of the concentration or partial pressure of carbon dioxide in the respiratory gases.

In healthy individuals, the difference between arterial blood and expired gas CO2 partial pressures is very small (normal difference 4-5 mmHg). When the measurement is taken at the end of a breath (exhaling), it is called "end tidal" CO2 (PETCO2).The capnogram is a direct monitor of the inhaled and exhaled concentration or partial pressure of CO2, and an indirect monitor of the CO2 partial pressure in the arterial blood. It is usually presented as a graph of CO2 (measured in kilopascals, "kPa" or millimeters of mercury, "mmHg") plotted against time, or, less commonly, but more usefully, expired volume (known as volumetric capnography). Its main development has been as a monitoring tool for use during anesthesia and intensive care. Wikipedia Rate this definition: 0.0 / 0 votesĬapnography is the monitoring of the concentration or partial pressure of carbon dioxide (CO2) in the respiratory gases.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
