

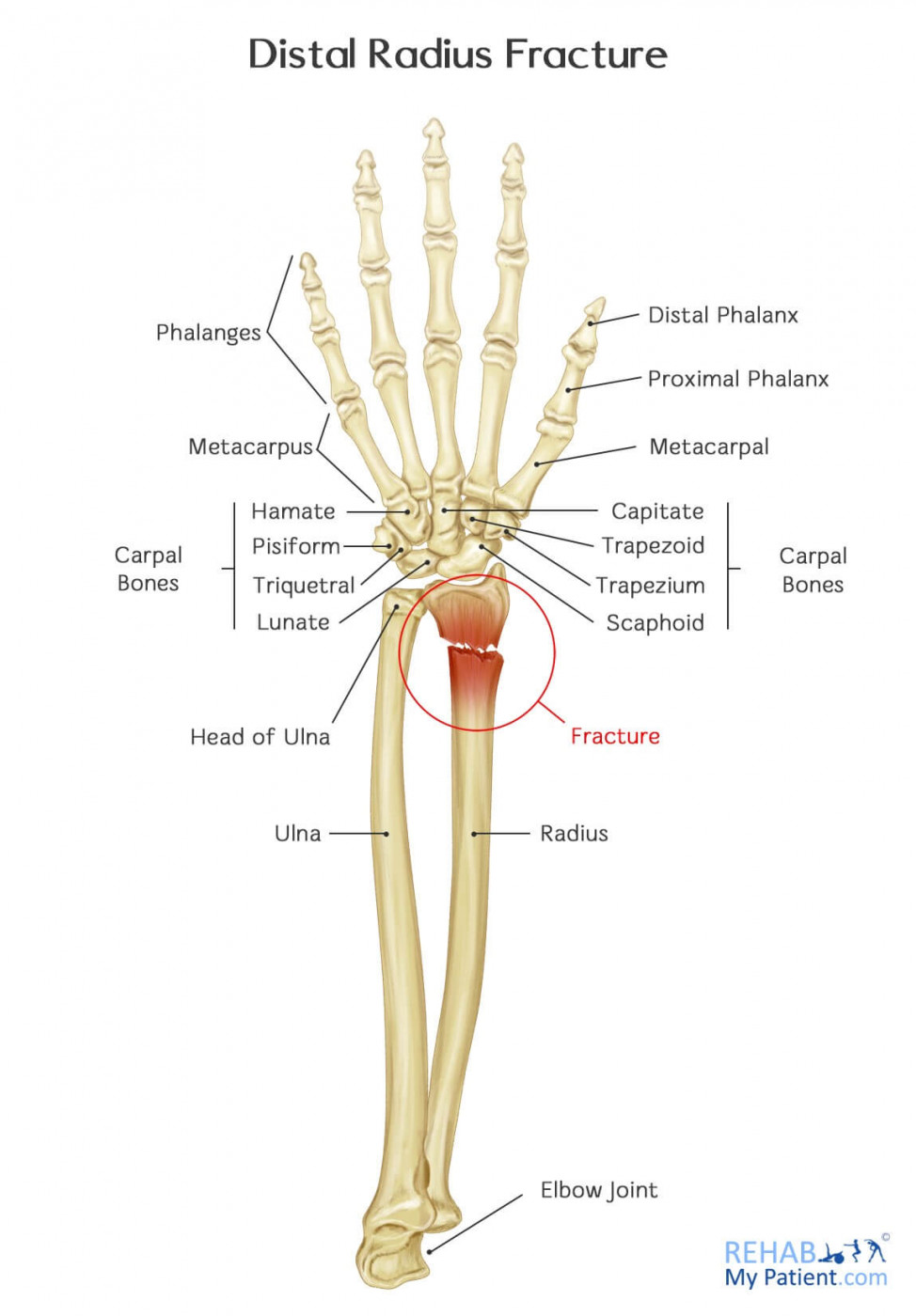
A scaphoid X-ray series should have four views.A wrist X-ray should have PA and lateral views and include the proximal half of the metacarpals and distal third of the radius and ulna.In children over 10 years of age, look for clinical signs of a scaphoid fracture: anatomical snuffbox tenderness, pain on axial compression of thumb, and pain on supination against resistance.Clinical deformity is usually evident in displaced fractures (most commonly dorsal displacement and angulation).Limitation in supination may be a sign of minor buckle fractures.

There is usually localised tenderness and swelling with decreased range of movement.The most common mechanism of injury is a fall onto an outstretched hand.
#Distal radius full#
R ead the full PCH Emergency Department disclaimer. Clinicians should also consider the local skill level available and their local area policies before following any guideline. These clinical guidelines should never be relied on as a substitute for proper assessment with respect to the particular circumstances of each case and the needs of each patient. Clinical common-sense should be applied at all times.
They are not strict protocols, and they do not replace the judgement of a senior clinician. These guidelines have been produced to guide clinical decision making for the medical, nursing and allied health staff of Perth Children’s Hospital. Fractures - Distal forearm or wrist Disclaimer


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
